05/06/2024 / Gynecology and Motherhood
Placental Abruption
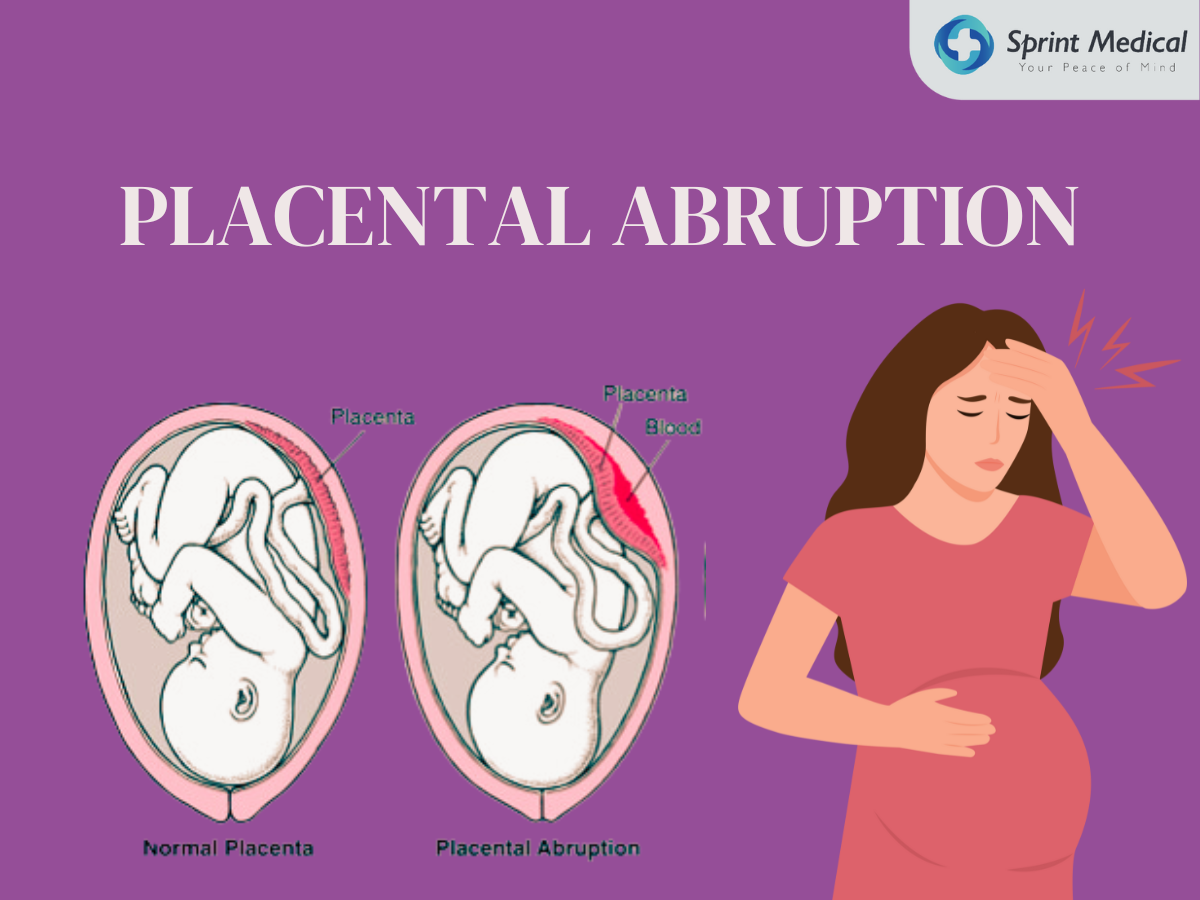
Placental abruption or abruptio placentae is a serious medical complication during pregnancy, it refers to a condition when the placenta separates from the uterus.
Dr Aditi Yadav
Table of Content
Introduction
Placental abruption or abruptio placentae is a serious medical complication during pregnancy, it refers to a condition when the placenta separates from the uterus. Vascular structures delivering oxygen and nutrient supply to the fetus are compromised. It can be due to high blood pressure or substance use leading to uterus stretching. The uterus is elastic and the placenta is stable. Stretching causes the vascular structures tearing that connect the uterus wall to the placenta. This condition usually occurs before 37 weeks gestation.
Types of Placental Abruption
Placental Abruption is classified based on the following:
Based on class
Class 0:
Asymptomatic (presence of blood clot, retrospective diagnosis).
Class 1:
Mild (None to mild vaginal bleeding, slight uterine tenderness, no fetal distress)
Class 2:
Moderate (none to moderate vaginal bleeding, uterine tenderness with tetanic contractions, changes in vital signs, fetal distress, hypofibrinogenemia)
Class 3:
Severe (none to severe vaginal bleeding, Tetanic uterus, Maternal shock hypofibrinogenemia and coagulopathy, fetal death)
Based on detachment:
Partial placental abruption:
The placenta is not completely detached from the uterine wall.
Total placental abruption:
The placenta is completely detached from the wall of the uterus. Vaginal bleeding occurs.
Based on bleeding
Revealed placental abruption:
Vaginal bleeding is moderate to severe.
Concealed placental abruptions:
Vaginal bleeding may not occur and even if it occurs it is mild. Blood is trapped between the placenta and uterine wall.
Signs and Symptoms of placental abruption
Symptoms are seen during the third trimester. They are:

Bleeding
Pain in abdomen
Back pain
Uterine contractions are long and intense
Uterine tenderness.
Less fetal movement
Vaginal bleeding
Mild cramping
What causes placental abruption
As mentioned by Schmidt; et al and colleagues, the following are the main causes of placental abruption:
Health history including behavior, past gynecological history, situation in current pregnancy (multiple gestation pregnancies, polyhydramnios, preeclampsia, sudden uterine decompression, and short umbilical cord)., trauma (fall, violence, accident), history of high blood pressure
Lifestyle factors like a history of smoking
Drug abuse history, consumption of cocaine during pregnancy.
Age is the top consideration during pregnancy as advancing maternal age, especially over 35 increases the risk of placental abruption.
There are many risk factors for placental abruption including Fibroid, blood clotting disorder, accident, abdominal trauma, infection of amniotic fluid, premature rupture of membranes.
Complications of placental abruption

Increases risk of maternal morbidity and perinatal mortality.
Hemorrhage (bleeding)
Blood transfusions,
Hysterectomy
Renal failure.
Preterm birth
Low birth weight
Anemia
Blood clotting issues
Growth problems
Stillbirth
Diagnosis
The following are the important points to consider while the diagnosis of placental abruption is established. Diagnosis and Tests of a placental abruption include:
Patient personal history including history of trauma to abdomen, cocaine, substance use
Past medical history including previous history of placental abruption
Physical examination:
Inspection for vaginal bleeding
Sonogram for placental location
Blood investigations like CBC, fibrinogen, and clotting profile, blood group.
Urine tests
Continuous electronic fetal monitoring
Ultrasound examination to determine the placental location
Treatment of placental abruption includes:

IV fluid and supplemental oxygen on arrival to hospital.
Continuous monitor of the mother and the fetus.
Delivery in case of class 2/class 3 classification
Emergency cesarean due to signs of fetal distress
Maintenance fluids and circulatory volume during surgery.
Prevention of placental abruption or abruptio placentae
Avoid substance use like cocaine
Avoid alcohol and smoking
Consult a dietician to make wise and healthy food choices
Follow a healthy lifestyle
Maintain blood pressure
Maintain a healthy lifestyle to prevent chronic diseases.
Prevent falls and trauma. Use a comfortable footwear and avoid wearing slippery footwear.
While driving wearing a seat belt.
Be alert always if you find any evidence of bleeding, contact your doctor immediately.
Conclusion
What is a placental abruption? Placental abruption, also known as abruptio placentae, is a serious obstetric complication associated with fetal distress, maternal shock and other complications. Age above 35, high blood pressure, previous history of abruption, and smoking are the risk factors associated. It is essential to recognize its risk factors and clinical presentations to manage the condition effectively and mitigate its severe consequences.
Related Posts
PREMATURE LABOR
Labor at term involves a normal physiological process, but premature labor is a pathological process. In this article, we will understand more on signs of premature labor, its causes, prevention, and more.
Dr Aditi Yadav
PCOS in Teenage Girls: Symptoms and Diagnosis
What is PCOS in Teenagers? Discover the symptoms, and know how to manage PCOS in Teenage Girls.
Diarrhea in Pregnancy - Treatment and Home Remedies for Diarrhea during Pregnancy
Get relief from diarrhea during pregnancy. Learn about safe treatment and home remedies to ensure a healthy pregnancy journey.
Does Female Masturbation Cause Infertility?
Female masturbation benefits in relieving mental and physical stress. Female masturbation is not harmful and female masturbation does not cause infertility in females.
Ovulation Pain (Mittelschmerz): Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
Ovulation pain also known as mittelschmerz is a dull ache or cramp in the lower abdomen around ovulation time.
Health & Wellness Tips
Subscribe to our blog